What is a 3D Printed Barcode?
A 3D printed barcode is a barcode that is created using three-dimensional printing technology.
Unlike traditional barcodes, which are typically printed on flat surfaces, 3D printed barcodes have a physical depth and can be made from various materials, providing enhanced durability and new functionalities.
Differences Between Traditional Barcodes and 3D Printed Barcodes
Traditional barcodes are two-dimensional, typically printed using ink on paper or labels. They are scanned using optical devices that read the pattern of lines or dots.
In contrast, 3D printed barcodes are physical objects with depth, created by layering material using a 3D printer. This adds a new dimension of durability and potential for integration with other technologies such as RFID and NFC.
How 3D Printing Technology Works?
Several types of 3D printers can be used to create barcodes, including:
● Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This is one of the most common types of 3D printing, where a thermoplastic filament is heated and extruded layer by layer.
● Stereolithography (SLA): This method uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid plastic, offering high precision and detail.
● Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): This technique uses a laser to sinter powdered material, such as nylon or metal, into a solid structure.
Materials Used for 3D Printing Barcodes
The choice of material depends on the application and desired durability. Common materials include:
● PLA (Polylactic Acid): A biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources, suitable for general use.
● ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): A strong, impact-resistant plastic, ideal for more demanding applications.
● Nylon: Known for its strength and flexibility, making it suitable for high-stress environments.
● Metal: Used for creating highly durable and tamper-proof barcodes.
Benefits of 3D Printed Barcodes
● Durability and Longevity Compared to Traditional Barcodes
3D printed barcodes are more durable than their traditional counterparts. They can withstand harsh environmental conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture, and physical abrasion, making them ideal for industrial and outdoor applications.
● Customizability and Flexibility in Design
3D printing allows for intricate and customized designs that are not possible with traditional printing methods. Barcodes can be designed to fit specific shapes and sizes, tailored to the unique needs of products and applications.
● Potential for Integration with Other Technologies
3D printed barcodes can be combined with other identification technologies like QR codes, RFID tags, and NFC chips. This integration provides multifaceted solutions for tracking, authentication, and data storage.
Applications of 3D Printed Barcodes
● Use in Manufacturing and Logistics
In manufacturing, 3D printed barcodes can be embedded directly into parts and products, ensuring they are traceable throughout the supply chain. This is particularly useful for high-value items and components that require stringent tracking.
● Applications in Retail and Inventory Management
Retailers can use 3D printed barcodes for inventory management, ensuring products are easily identifiable and traceable from the warehouse to the store shelf. The durability of 3D printed barcodes ensures they remain readable even in high-traffic environments.
● Healthcare and Pharmaceutical Uses
In healthcare, 3D printed barcodes can be used on medical devices and pharmaceutical products to enhance traceability and combat counterfeiting. This ensures that medical professionals can verify the authenticity and history of critical supplies and medications.
● Innovative Uses in Product Packaging and Marketing
3D printed barcodes can be incorporated into product packaging, offering a unique marketing tool. Brands can create custom, eye-catching designs that not only serve as barcodes but also enhance the visual appeal of their packaging.
How to Generate a 3D Printed Barcode?
1. Choosing the Barcode Generator: Use an online barcode generator.
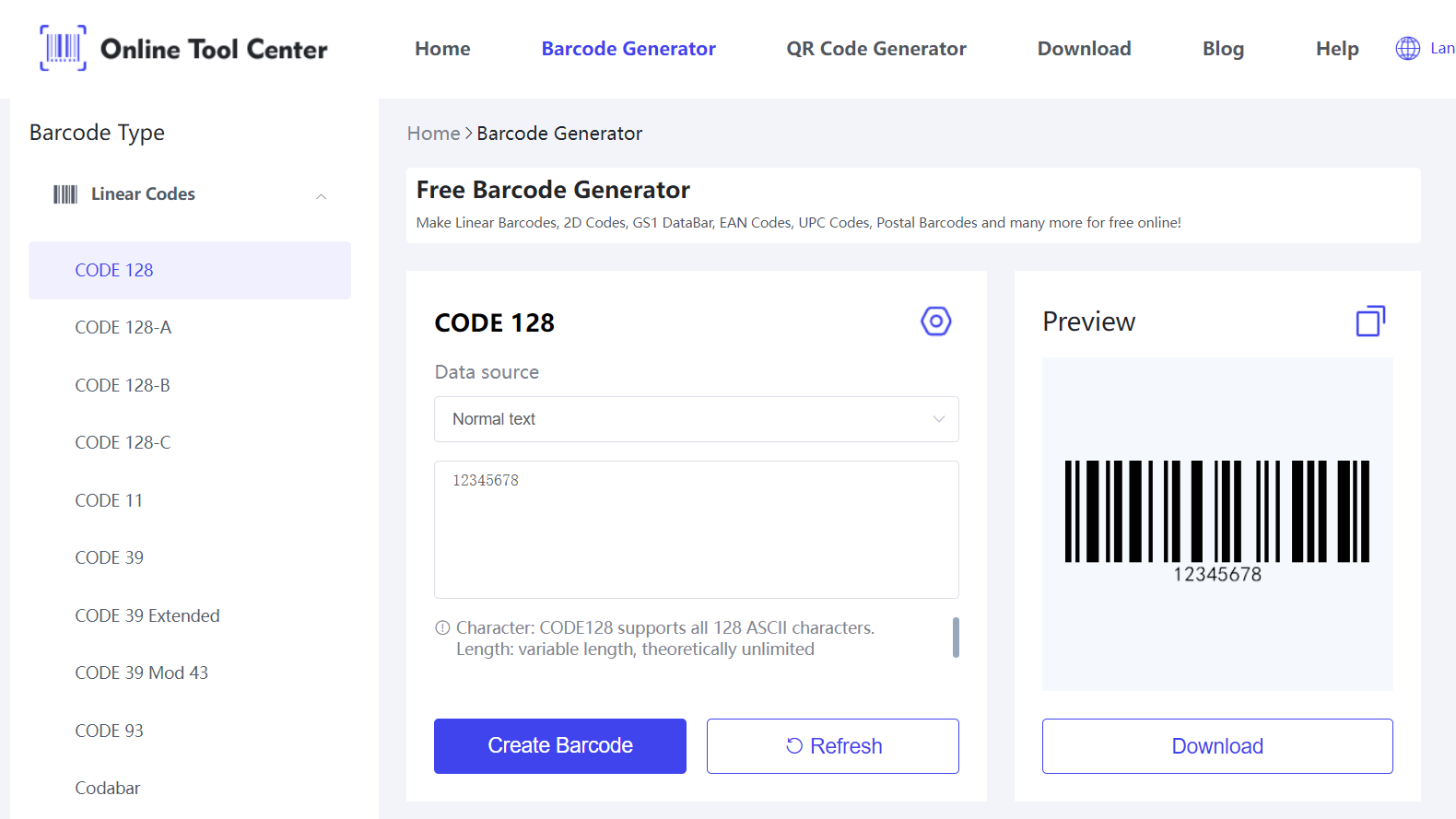
2. Designing the Barcode Using CAD Software: Import the generated barcode into CAD software to create a 3D model.
3. Setting Up the 3D Printer: Configure your 3D printer according to the material and design requirements.
4. Printing the Barcode: Begin the printing process, ensuring the printer is calibrated correctly for accuracy.
5. Testing the Barcode: After printing, test the barcode with a barcode scanner to ensure it is readable and functional.
Case Studies
Several companies across different industries have successfully implemented 3D printed barcodes. For example, a leading automotive manufacturer has integrated 3D printed barcodes into their parts to improve traceability and reduce counterfeiting. Similarly, a pharmaceutical company uses 3D printed barcodes on packaging to enhance security and ensure product authenticity.
In summary, 3D printed barcodes represent a significant advancement in barcode technology.
As technology continues to evolve, 3D printed barcodes are set to play a crucial role in the future of inventory management and product identification.
Start exploring the potential of 3D printed barcodes today with our free barcode generator!
FAQs
1. Can you 3D print a barcode?
Yes, you can 3D print a barcode using appropriate 3D printing technology and materials. The process involves creating a 3D model of the barcode and printing it using a 3D printer.
2. Can you 3D print a working QR code?
Yes, it is possible to 3D print a QR code. The QR code must be accurately designed and printed to ensure it is scannable.
3. What is the difference between a 3D barcode and a QR code?
A 3D barcode is a physical object with depth created using 3D printing, while a QR code is a two-dimensional code that can store more information than traditional barcodes.
Both can be used for tracking and identification, but 3D barcodes offer enhanced durability and security.




