In modern business, barcode technology has become essential due to its speed, accuracy, and efficiency. The role of barcodes is evident across multiple functions, including product management, logistics tracking, and retail checkout, significantly optimizing business operations. But what is the role of barcodes, and how have they transformed traditional management processes?
What Is a Barcode?
A barcode is a machine-readable code consisting of alternating black and white lines or squares that encode information. Its primary function is to quickly and accurately scan and recognize data via scanning devices. Barcodes come in two types:
● One-dimensional (1D) barcodes: Examples include EAN-13 and UPC. These are primarily used to uniquely identify retail products and store short data, such as numeric codes or alphanumeric characters.
● Two-dimensional (2D) barcodes: Examples include QR codes. These can store more complex information, such as URLs, text, or multimedia files, and are widely used for applications like mobile payments and marketing.

The Role of Barcodes in Business
Barcodes have wide-ranging applications that streamline operations, reduce errors, and increase efficiency. Below, we examine the role of barcodes with specific examples across various industries.
1. Product Management
The role of barcodes in product management is especially prominent in retail. Printing barcodes on product packaging allows businesses to quickly enter product information and automatically update inventory records, reducing the risk of human error.
For instance, in large supermarkets or e-commerce warehouses, barcodes enable rapid scanning for inventory management. At the checkout, scanners automatically identify the barcode, retrieve pricing information, and update stock levels. This process speeds up transactions and ensures real-time inventory updates.
In the apparel industry, brands use barcodes to track a product's lifecycle from production to sale, ensuring traceability. A high-end clothing brand, for example, places barcoded labels on each item, enabling monitoring from manufacturing to retail and customer experience.
2. Logistics Tracking
Barcodes are key to improving supply chain efficiency. Each package or item in transit is tagged with a unique barcode, allowing logistics companies to scan and update package statuses in real-time.
For example, courier companies like DHL and FedEx rely on barcode technology to monitor package shipments. Each package carries a unique barcode, which, when scanned, provides real-time tracking information, including location, estimated delivery times, and any delays. This transparency boosts customer satisfaction and optimizes logistics operations.
Barcodes also improve warehouse management. Workers can scan barcodes to quickly locate and dispatch items, minimizing errors and reducing time spent searching for goods. E-commerce platforms, for example, use barcode scanning to streamline order fulfillment, allowing staff to quickly find and ship products.
3. Retail Checkout
In retail environments, barcodes play a crucial role in speeding up the checkout process. Using barcode scanners, cashiers can instantly retrieve product information, eliminating the need for manual price entry and improving checkout speed.
For example, in large retailers like Walmart, each item has a barcode label. When customers check out, the cashier scans the barcode, and the system automatically calculates the total price. This improves the checkout experience, reduces inventory errors, and generates accurate sales data for later analysis.
Furthermore, barcodes provide valuable insights into customer purchasing behavior. Retailers can use this data to identify popular products, optimize inventory levels, and adjust marketing strategies.
Best Practices for Printing Barcodes
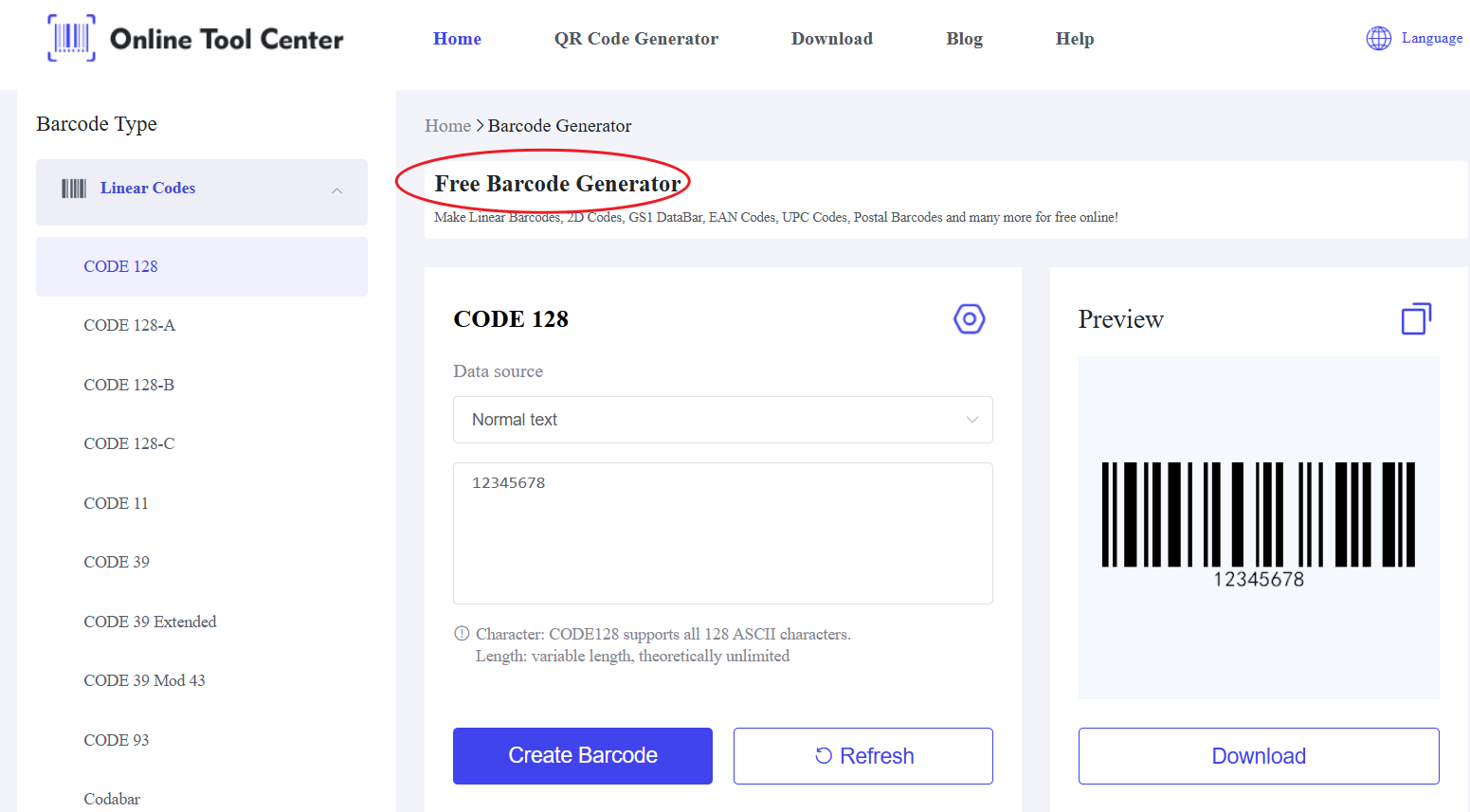
For barcodes to function properly, print quality is essential. Here are some best practices for barcode printing:
1. Choose the correct barcode type: Select the appropriate 1D or 2D barcode format based on the amount of information you need to encode. Ensure the format suits the intended use case.
2. Ensure high print resolution: Poor resolution can make barcodes difficult or impossible for scanners to read. High-resolution printers, such as thermal or laser printers, are recommended for clear, scannable barcodes.
3. Test barcode readability: After printing, test the barcodes with a scanner to ensure they are legible under different lighting conditions.
For businesses seeking high-quality barcode generation, we recommend the free barcode generator from our website. This tool allows you to create both 1D and 2D barcodes quickly and easily, without needing additional software.
Barcode technology has significantly transformed modern business practices. By fully understanding and utilizing the role of barcodes, companies can optimize product management, logistics tracking, and customer service processes.
If you're looking for a reliable and easy-to-use barcode generation tool, try the free barcode generator to simplify your workflow.





