What Are Barcode Scanners Called?
When we talk about technology that streamlines inventory, checkout, or shipping processes, barcode scanners come up often.
But technically, what are barcode scanners called? Common terms include barcode readers, scanning devices, or simply scanners. These devices decode information embedded in barcodes and feed that data into a computer system, reducing human error and speeding up operations.
Let's explore the various terms and types of barcode scanners, how they work, and their essential role in different industries.
Common Names for Barcode Scanners
When asking what are barcode scanners called, you might encounter several alternative names, each highlighting a different aspect of the device's function or design:
● Barcode Reader: A general term for any device that decodes barcodes. This can refer to handheld or stationary models.
● POS (Point of Sale) Scanner: This term is often used in retail environments, where scanners are integrated with POS systems.
● Imager: A specific type of scanner that captures the barcode as an image rather than using traditional laser technology. These are especially useful for reading 2D barcodes like QR codes.
● Handheld Barcode Scanner: A widely-used term for portable scanners that workers can easily carry. These are common in inventory management and warehousing.
Regardless of the specific terminology, all these devices serve the same purpose: to quickly and accurately interpret barcode data.
Types of Barcode Scanners
Understanding the different types of barcode scanners helps you select the best option based on your industry needs. Each type of scanner uses different technology to read and process barcodes:
1. Laser Scanners
Laser scanners are the most widely used type of barcode scanner. They work by projecting a thin laser beam that moves across the barcode.
As the laser reflects off the barcode's black and white lines, the scanner reads the reflected light to decode the information. These scanners are known for being reliable, fast, and effective at reading barcodes from various distances, which makes them a top choice in retail and warehousing.
2. CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) Scanners
CCD scanners, also calle linear imagers, capture the entire barcode at once using multiple light sensors. Unlike laser scanners, which scan one line at a time, CCD scanners read the entire barcode instantly.
They're known for their durability and reliability, particularly in environments where barcodes need to be scanned frequently, like in point-of-sale terminals.
3. 2D Image Scanners
2D image scanners use advanced technology to capture a picture of the barcode, making them highly versatile. These scanners can read both 1D and 2D barcodes, such as QR codes, which store more data than traditional barcodes. Because 2D image scanners can read barcodes from any angle, they're ideal in situations where speed and flexibility are essential, such as healthcare and logistics.
4. Omnidirectional Scanners
Commonly found in grocery stores and retail environments, omnidirectional scanners project multiple laser lines in all directions. This allows them to scan barcodes without needing the perfect alignment between the barcode and the scanner.
Omnidirectional scanners speed up the checkout process, making them highly valuable in fast-paced retail environments.
How Barcode Scanners Work
All barcode scanners share a similar operational structure, despite their different technologies:
1. Light Emission: The scanner emits a beam of light, which is either a laser or LED, aimed at the barcode.
2. Reflection and Capture: The light reflects off the barcode and back into the scanner's sensor. The white spaces in the barcode reflect more light, while the black bars absorb it.
3. Decoding: The sensor converts the reflected light into an electrical signal. The scanner's decoder processes this signal and translates it into readable information, which is then sent to a computer or POS system.
This process happens in milliseconds, enabling fast, accurate data entry without human error.
Popular Uses of Barcode Scanners
Barcode scanners are indispensable tools across many industries, each requiring different features depending on the application. Below are specific examples of how barcode scanners are used:
1. Retail
In retail, barcode scanners are used at checkout counters to quickly scan products and retrieve pricing information.
The integration with POS systems means transactions are processed efficiently, reducing wait times for customers. Barcode scanners also help in inventory management, ensuring that stock levels are updated when items are sold.
2. Healthcare
In hospitals and clinics, barcode scanners play a crucial role in patient safety and medication management. Scanning patient wristbands and medication barcodes helps prevent administration errors, ensuring the right patient gets the correct medication at the correct dose.
Additionally, scanners are used to track medical supplies and equipment, enhancing the overall operational efficiency of healthcare facilities.
3. Warehousing and Logistics
Warehouses rely heavily on barcode scanners to manage inventory, track shipments, and ensure accurate order fulfillment. Scanners help reduce the chances of picking errors and ensure real-time inventory updates.
Logistics companies use barcode scanning systems to track parcels, ensuring that every package is accounted for during its journey.
4. Manufacturing
In manufacturing, barcode scanners track parts and materials at different stages of the production process.
By scanning barcodes, manufacturers can ensure quality control, monitor productivity, and track the movement of components through the assembly line. This data is essential for optimizing workflows and maintaining supply chain efficiency.
5. Libraries
In libraries, barcode scanners are used to manage the borrowing and returning of books. Each book and borrower is assigned a unique barcode, which streamlines the check-in and check-out process and keeps the library's inventory accurate and up to date.
To summarize, answering what are barcode scanners called depends on their specific application, with terms like barcode reader, POS scanner, and imager being commonly used. Each type of barcode scanner has unique features designed to meet the demands of different industries, from retail to healthcare.
Choosing the right barcode scanner is only one part of the process. Before scanning, you need a way to create your barcodes. A free online barcode generator allows businesses to generate barcodes for products, inventory, or asset tracking with ease.
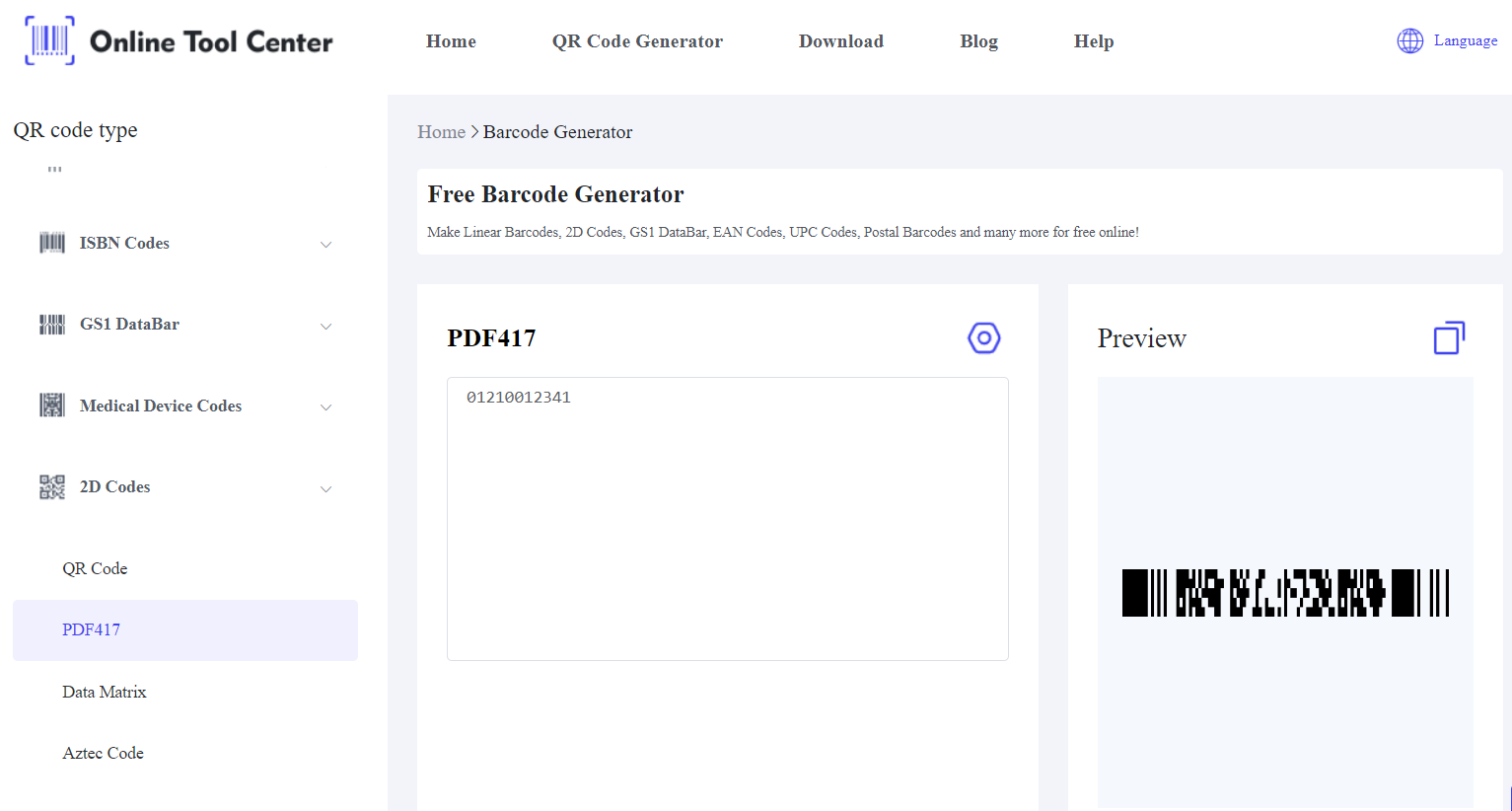
By using the online barcode generator alongside the appropriate barcode scanner, you can ensure accurate data entry, streamlined operations, and overall improved business efficiency.





