Barcodes are an integral part of modern business and daily life, enabling efficient tracking, identification, and management of products and information.
In this article, we will explore different barcode examples, their types, and practical applications. By understanding these examples, you can better appreciate the role of barcodes and how they can streamline operations.
What is a Barcode?
A barcode is a machine-readable representation of data, typically displayed in a linear or two-dimensional pattern. It consists of a series of parallel lines (bars) and spaces of varying widths that encode information. Barcodes can store various types of data, including product numbers, serial numbers, and batch numbers.
Common Types of Barcodes
There are several types of barcodes, each serving different purposes. Here are some common barcode examples:
1. UPC: Commonly found on retail products in the United States, the UPC barcode encodes a 12-digit number that identifies a product and its manufacturer.
Example: UPC-A - 036000291452

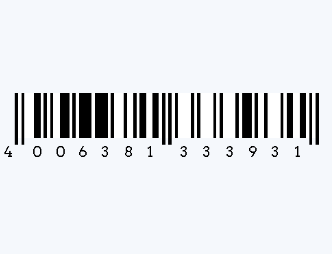
2. EAN: Similar to the UPC, the EAN is used internationally and typically encodes a 13-digit number.
Example: EAN-13 - 4006381333931
3. Code 39: This alphanumeric barcode is widely used in various industries for inventory and tracking purposes. It can encode both letters and numbers, making it versatile.
Example: Code 39 - CODE39EXAMPLE

4. QR Code: A two-dimensional barcode that can store a large amount of data, including URLs, contact information, and more. It is commonly used in marketing and mobile applications.
Example: QR Code

Practical Barcode Examples
Barcodes are used in numerous ways across different industries. Here are a few barcode examples that illustrate their versatility:
1. Retail and Inventory Management
In retail, barcodes are essential for managing inventory and speeding up the checkout process. When a product is scanned at the point of sale, the barcode provides information about the product, including its price and description.
2. Healthcare
Barcodes play a crucial role in the healthcare industry by ensuring patient safety and improving efficiency. Medication labels often include barcodes that healthcare professionals scan to verify the correct medication and dosage.
Patient wristbands with barcodes help confirm patient identity and track medical records.
3. Logistics and Shipping
Barcodes are indispensable in logistics for tracking shipments and managing warehouse operations. Each package is assigned a unique barcode that provides details about its contents, destination, and tracking history. This ensures accurate and timely delivery of goods.
4. Libraries
Libraries use barcodes to manage their collections. Each book is tagged with a barcode that includes information such as the title, author, and catalog number. This simplifies the borrowing and returning process, allowing for efficient tracking of books.
How to Generate Barcodes?
Creating barcodes is straightforward with the help of a barcode generator that allows users to generate various types of barcodes for free. Here's a simple guide to creating your barcode:
1. Select the Type of Barcode: Choose the type of barcode that best suits your needs (e.g., UPC, EAN, QR Code).
2. Enter the Data: Input the information you want to encode in the barcode.
3. Customize the Design: Some tools allow you to adjust the size, color, and format of the barcode.
4. Generate and Download: Click the generate button, and your barcode will be created. You can then download it for printing or digital use.
In summary, barcodes are a powerful tool for businesses and organizations, offering a reliable method for tracking and managing information.
By exploring different barcode examples, you can better understand how to leverage this technology to improve efficiency and accuracy in various applications.
Whether you're in retail, healthcare, logistics, or any other industry, a barcode generator can help you create the barcodes you need quickly and easily.
Try generating your barcodes today with our barcode generator and experience the benefits firsthand.
By integrating barcode examples into your operations, you can streamline processes, reduce errors, and enhance overall productivity.




