What is the Difference Between 1D vs 2D Barcodes?
As barcode technology evolves, two primary formats have emerged: 1D vs 2D barcodes. Understanding the differences between these two barcode types is essential for selecting the right technology for your business or project.
What is a 1D Barcode?
A 1D barcode, also known as a linear barcode, is the traditional barcode most commonly seen on retail items. It consists of a series of parallel lines of varying widths and spaces. Each pattern of lines represents a sequence of numbers or characters that can be read by a scanner.
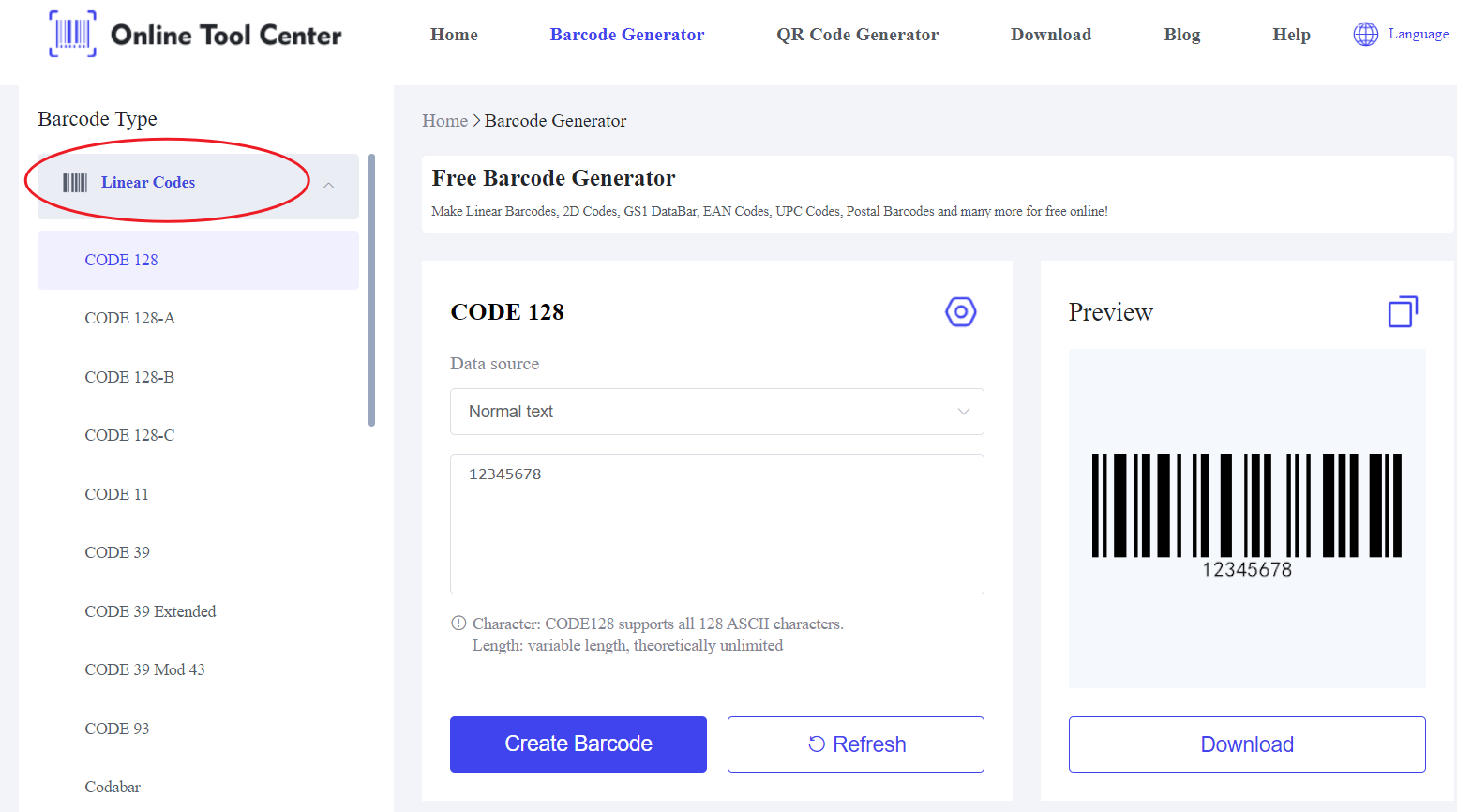
Key Features of 1D Barcodes:
● Data Capacity: A 1D barcode stores data horizontally, which restricts its capacity to a maximum of around 85 characters, depending on the specific barcode type (such as UPC or Code 39).
● Structure: The data is encoded in the width and spacing of the vertical lines. Each digit or letter has a corresponding line pattern.
● Scanning Technology: 1D barcodes require a laser scanner to interpret the information. The scanner reads the barcode in a single, horizontal pass.
● Common Applications: 1D barcodes are typically used in retail environments, where minimal data, usually just a product ID or SKU, is needed to identify an item at the point of sale.
What is a 2D Barcode?
Unlike its linear counterpart, a 2D barcode encodes data both horizontally and vertically, which dramatically increases its storage capacity. These barcodes can be recognized by their grid-like patterns, often appearing as squares, dots, or hexagons. A well-known example of a 2D barcode is the QR code, used in marketing, logistics, and even everyday tasks like digital payments.
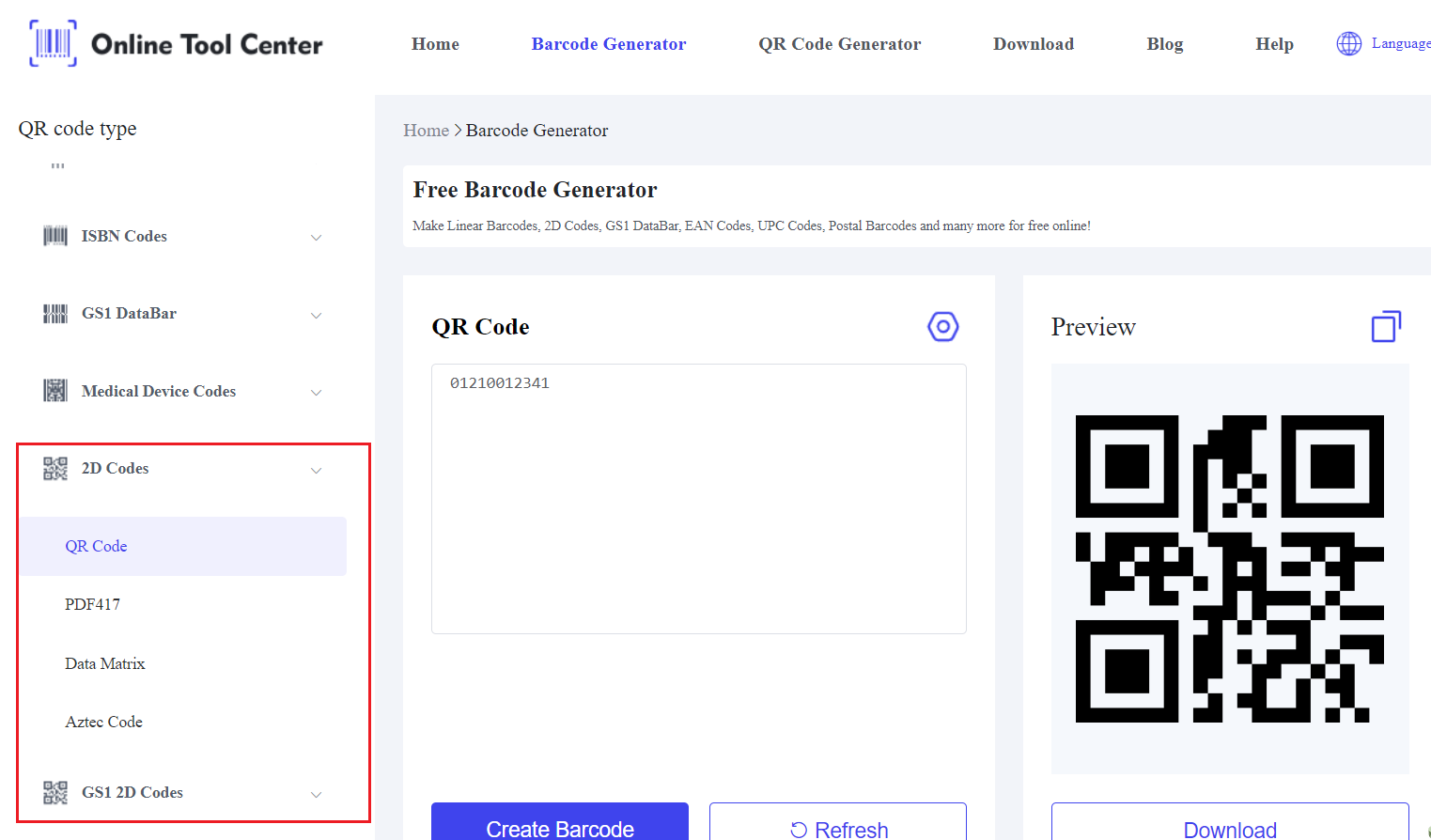
Key Features of 2D Barcodes:
● Data Capacity: A 2D barcode can store thousands of characters, making it suitable for storing more complex data like URLs, product specifications, or even encrypted information.
● Structure: The data is stored across two dimensions (horizontally and vertically), allowing for compact, high-density storage. This design is what enables 2D barcodes to hold so much more information than 1D barcodes.
● Scanning Technology: Unlike 1D barcodes, which require laser scanners, 2D barcodes can be scanned by both laser and imaging devices, including smartphone cameras.
● Common Applications: 2D barcodes are frequently used in logistics, healthcare, and marketing. For example, in the healthcare industry, 2D barcodes are used to store patient information on wristbands, ensuring accurate data is available during critical care.
What is the Difference Between 1D Barcode vs 2D barcodes?
When comparing 1D barcodes vs 2D barcodes, there are several critical factors that businesses must consider. Each barcode type has its strengths and weaknesses, making it suitable for different applications.
1. Data Capacity
The most apparent difference between 1D barcodes and 2D barcodes is their data capacity.
1D barcodes are limited to around 85 characters of information. This is sufficient for applications where basic identification is required, such as identifying a product or a serial number.
2D barcodes can store up to 7,000 characters, enabling them to encode more detailed information such as product descriptions, URLs, serial numbers, and even full addresses. This makes 2D barcodes more versatile in industries that require detailed tracking and identification.
2. Space Efficiency
1D barcodes grow longer as more information is encoded, which can be a drawback when space is limited. This is why products with small packaging, like pharmaceuticals, often avoid using 1D barcodes.
In contrast, 2D barcodes store vast amounts of information in a compact square or rectangular shape. The ability to store more data in a smaller footprint is one reason why 2D barcodes are preferred in industries like electronics, healthcare, and logistics.
3. Error Correction
1D barcodes lack built-in error correction. If a portion of the barcode is damaged or obscured, the entire barcode may become unreadable.
2D barcodes feature error correction, meaning they can still be scanned even if a part of the code is missing or damaged. This feature makes 2D barcodes highly reliable in harsh environments, such as warehouses or outdoor logistics, where labels may experience wear and tear.
4. Versatility and Scanning
1D barcodes require precise alignment with the scanner, which may slow down scanning in fast-paced environments.
2D barcodes, thanks to their grid-like structure, can be scanned from any angle and distance. This flexibility makes them suitable for modern devices such as smartphones, tablets, and other imaging devices, offering greater user convenience.
5. Application Specific Uses
1D barcodes are best suited for retail and basic inventory tracking, where only a small amount of data needs to be encoded.
2D barcodes are increasingly used in industries that demand more advanced applications. For example, in supply chain management, 2D barcodes provide detailed product tracking from manufacturing to delivery, while in healthcare, they encode critical patient data to ensure medical accuracy.
Why 2D Barcodes Are Better Than 1D
For many applications, 2D barcodes are simply more efficient and versatile than 1D barcodes. Their ability to store more data, combined with error correction and compact size, gives them a clear edge.
Additionally, the widespread use of smartphones as barcode scanners makes 2D barcodes more accessible for both businesses and consumers.
For businesses handling complex data, such as in the logistics, healthcare, or manufacturing sectors, the benefits of using 2D barcodes far outweigh the limitations of 1D barcodes.
Generating the Right Barcode for Your Needs
Choosing between a 1D vs 2D barcode comes down to your specific use case. For retail operations or basic inventory control, a 1D barcode might be sufficient.
However, for businesses that require more complex data encoding, or are operating in industries where durability and error correction are essential, 2D barcodes are the superior option.
If you're ready to create your barcode, consider using a barcode generator. This tool allows you to easily generate 1D and 2D barcodes to suit your specific needs, whether you're managing inventory, creating marketing campaigns, or streamlining logistics.
To wrap up, understanding the key differences between 1D vs 2D barcodes can significantly impact your business operations.
While 1D barcodes still have their place in basic retail and inventory applications, the versatility and data capacity of 2D barcodes make them a better choice for modern, data-rich environments.
Whether you need a simple product identifier or a high-capacity barcode for complex tracking, the right barcode generator can help you create the ideal solution.





