Effective inventory management is the backbone of any successful retail or manufacturing operation. The SKU barcode is a crucial element that ensures the smooth tracking and organization of products.
This guide will help you understand the role of SKU barcodes in streamlining inventory processes, their benefits, and how to generate them efficiently using a barcode generator.
What is an SKU and How Does It Relate to Barcodes?
SKU stands for Stock Keeping Unit, a unique identifier assigned to each product a business sells or manages. Unlike UPCs (Universal Product Codes), standardized across all businesses and industries, SKUs are company-specific.
They are typically alphanumeric codes designed to reflect product features like category, color, size, and other distinguishing attributes.
A barcode, on the other hand, is a visual representation of the SKU or other product data, encoded into a format that can be read by machines. When combined, an SKU barcode enables quick scanning and real-time access to critical information about a product.
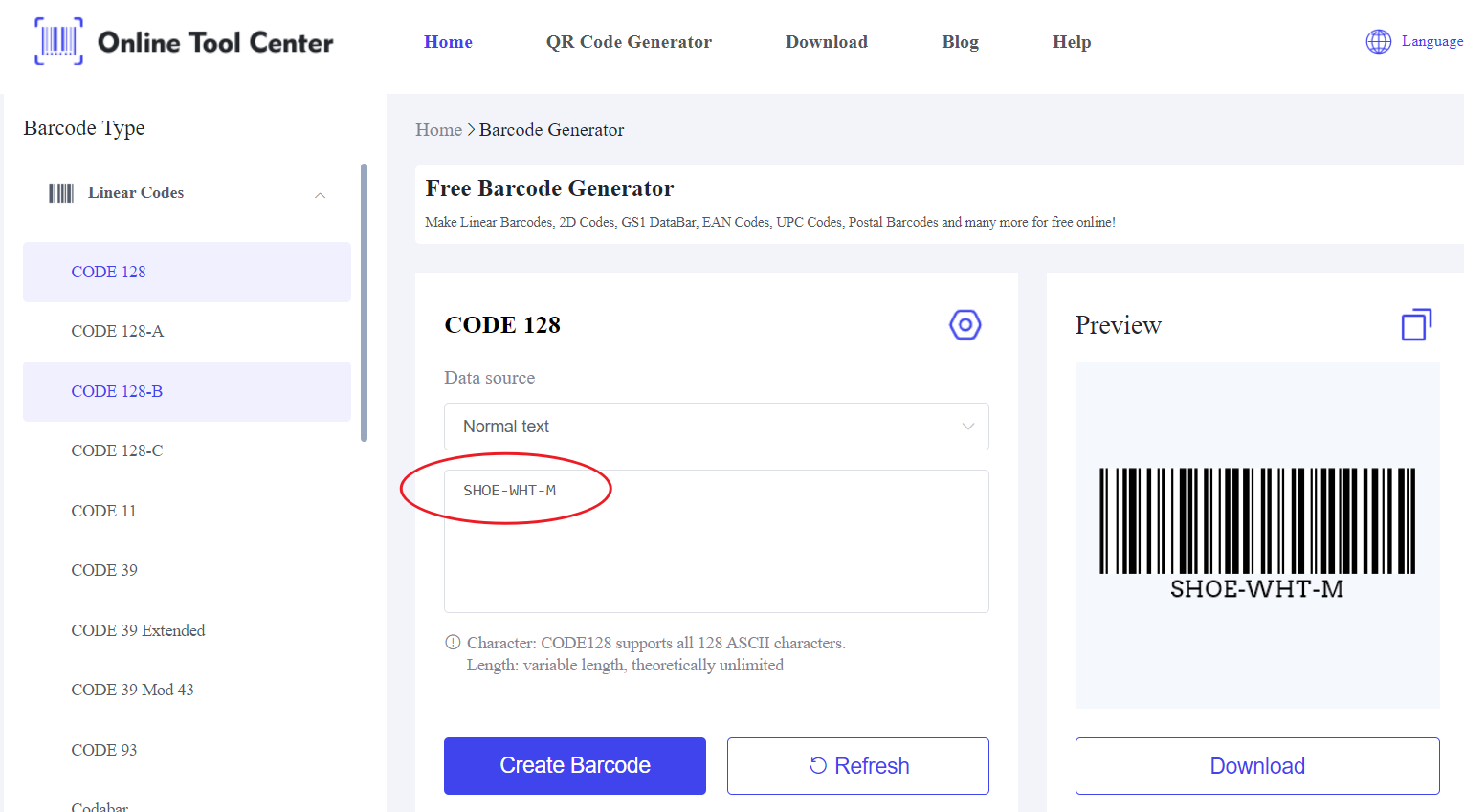
For example, an SKU might look like this: "SHOE-WHT-M" (for a medium-sized, white shoe), and when this SKU is converted into a barcode format (such as Code 128 or UPC-A), it can be scanned to retrieve details about that specific item instantly.
Why Are SKU Barcodes Crucial for Business Efficiency?
The integration of SKU barcodes into your inventory system provides significant advantages:
1. Enhanced Accuracy in Inventory Tracking
Manual product tracking is prone to human error. With an SKU barcode, products can be scanned quickly and accurately, reducing mistakes during stock counts, shipments, and restocking. A well-implemented SKU barcode system minimizes mislabeling and data entry errors.
2. Streamlined Operations
A barcode system connected to your inventory management or enterprise resource planning (ERP) software allows for updates when products are scanned.
This capability is particularly valuable in environments like retail stores or large warehouses, where rapid identification of stock is essential for fulfilling orders, processing returns, or restocking shelves.
3. Better Demand Forecasting and Reordering
By leveraging data from SKU barcodes, businesses can track which items are selling faster, which ones are underperforming, and when stock is low.
This level of insight simplifies reordering and helps in adjusting stock levels based on real-time demand, ensuring that the right products are always available when customers need them.
4. Improved Customer Service and Experience
With an SKU barcode system, your staff can quickly check product availability, locate items within a warehouse, and process transactions more efficiently. This means fewer delays and improved service, which ultimately enhances customer satisfaction.
Different Types of Barcodes for SKU Identification
Not all barcodes are the same. Depending on your business needs, the SKU barcode you use may differ in format. Here are a few of the most common types:
● UPC (Universal Product Code): Mostly used for retail products in North America. It is standardized, meaning each product's UPC code is the same across all businesses.
● EAN (European Article Number): Similar to UPC but widely used internationally, especially in Europe.
● Code 128: A flexible, high-density barcode often used for internal tracking within a company. It's ideal for SKU barcodes as it can encode both letters and numbers.
How to Generate an SKU Barcode?
Step 1: Create Your SKU
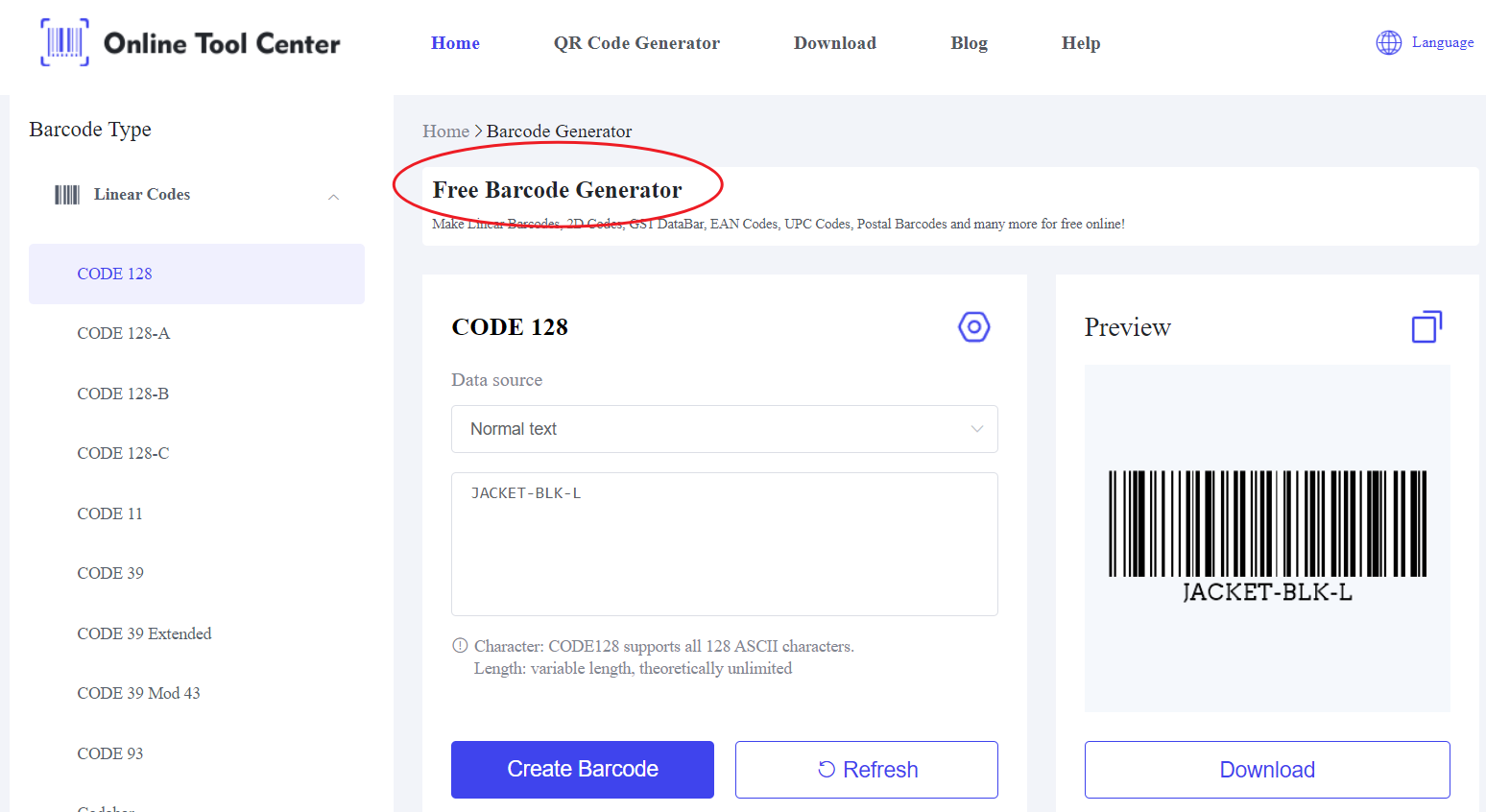
The first step is to develop a consistent SKU format for your products. Ensure your SKUs contain relevant product information, such as the category, size, or color. For example, "JACKET-BLK-L" could represent a large black jacket.
Step 2: Select the Barcode Format
Choose the correct barcode format that suits your business needs. For inventory and internal tracking purposes, Code 128 is often recommended because of its flexibility to encode both numeric and alphanumeric characters.
Step 3: Use a Barcode Generator
Input your SKU into the SKU barcode generator. The generator will automatically convert your SKU into a scannable barcode. Be sure to select the correct format and size that your barcode scanners can read efficiently.
Step 4: Print and Apply the Barcode
After generating your SKU barcode, use thermal label printers to print it on adhesive labels or employ coding machines to mark it directly on the packaging.
Once applied, the barcode should be easily scannable to integrate seamlessly with your existing inventory system.
Best Practices for Using SKU Barcodes
To maximize the effectiveness of your SKU barcode system, consider the following best practices:
● Maintain Consistency: Ensure that your SKU creation follows a standardized structure, avoiding any duplicates or irregularities.
● Test Barcode Scanning: Regularly check that your barcodes are easily scannable. Poor printing quality or inappropriate barcode sizing can lead to scanning issues.
● Integrate with Inventory Management Software: Use a system that integrates barcodes directly into your inventory management or ERP solution.
In summary, implementing an SKU barcode system is one of the most effective ways to streamline inventory management, reduce errors, and improve operational efficiency.
By using an SKU barcode generator, you can easily create barcodes for all your products and ensure they are tracked accurately within your system.
Try generating your SKU barcodes with a trusted barcode generator and take your inventory management to the next level.




