How to Make an Intelligent Mail Matrix Barcode (IMmb)
In the evolving landscape of mail processing, the Intelligent Mail Matrix Barcode (IMmb) has emerged as a robust solution to enhance package visibility and processing efficiency.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the IMmb, its benefits, and a step-by-step approach to creating and implementing it in your mailing operations.
Understanding the Intelligent Mail Matrix Barcode (IMmb)
The IMmb is a two-dimensional barcode utilizing the GS1 DataMatrix symbology, developed by the United States Postal Service (USPS) to improve the routing and tracking of packages.
Unlike the traditional linear Intelligent Mail Package Barcode (IMpb), the IMmb offers a more compact and robust encoding method, making it particularly effective for packages that are irregularly shaped or prone to label distortion during automated processing.
Key Features:
● Data Redundancy: The IMmb contains the same data as the IMpb but allows for the inclusion of two additional IMmbs within unused areas of existing standard shipping labels.
This redundancy provides sorters with multiple opportunities to read the barcode, thereby enhancing package visibility and reducing the likelihood of processing errors.
● Space Efficiency: The smaller footprint of the IMmb enables its placement in areas of the label that are less susceptible to damage or distortion, ensuring better scan rates even under challenging conditions.
Differences Between Intelligent Mail Matrix Barcode (IMmb) and Intelligent Mail Barcode (IMb)
While both the IMmb and the Intelligent Mail Barcode (IMb) are utilized within the USPS system, they serve different purposes and possess distinct characteristics:
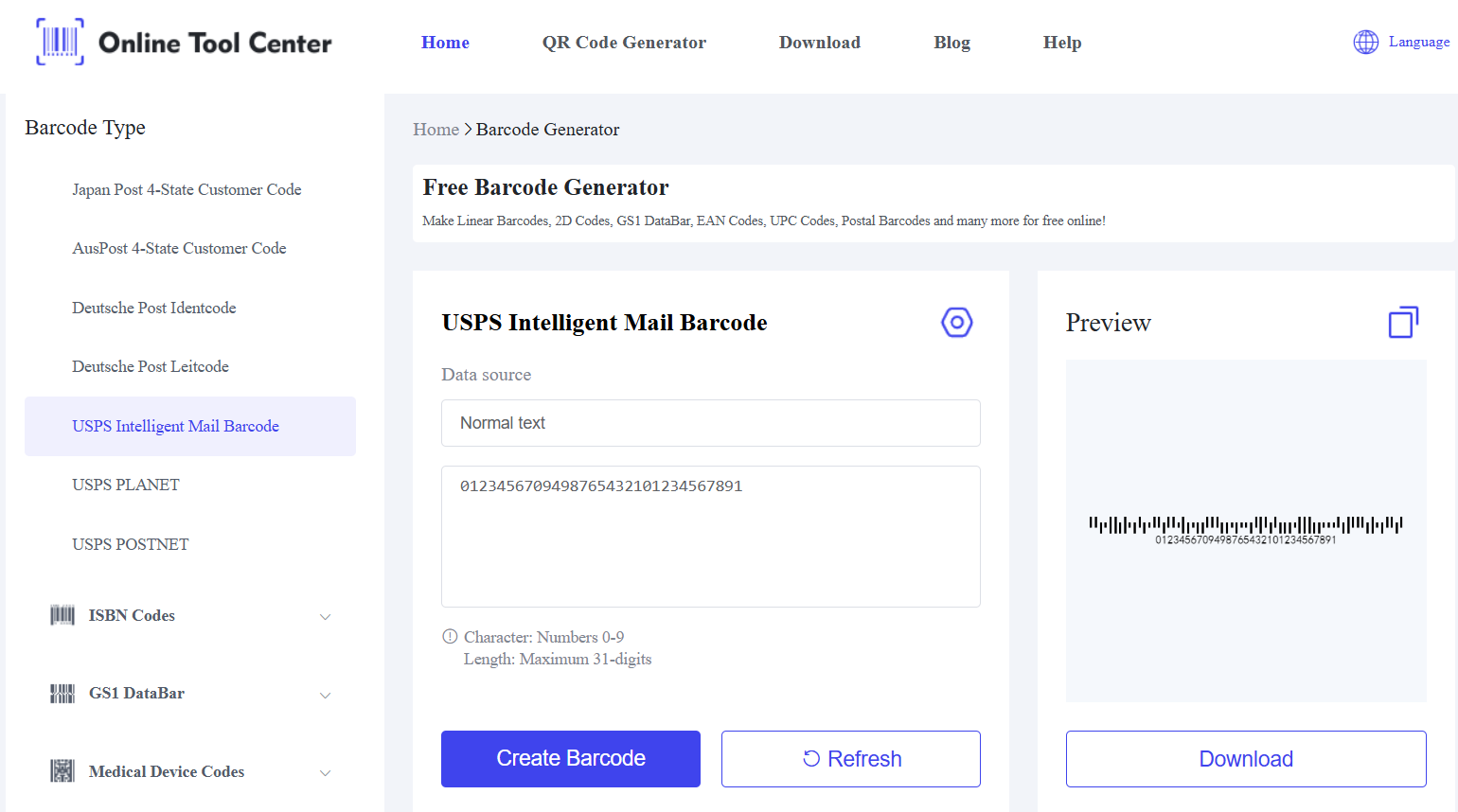
1. Barcode Type: The IMb is a linear barcode consisting of 65 bars, each varying in height to encode data, and is primarily used for sorting and tracking letters and flat mail pieces.
In contrast, the IMmb is a two-dimensional (2D) barcode that employs the GS1 DataMatrix symbology, allowing for higher data density and improved error correction.
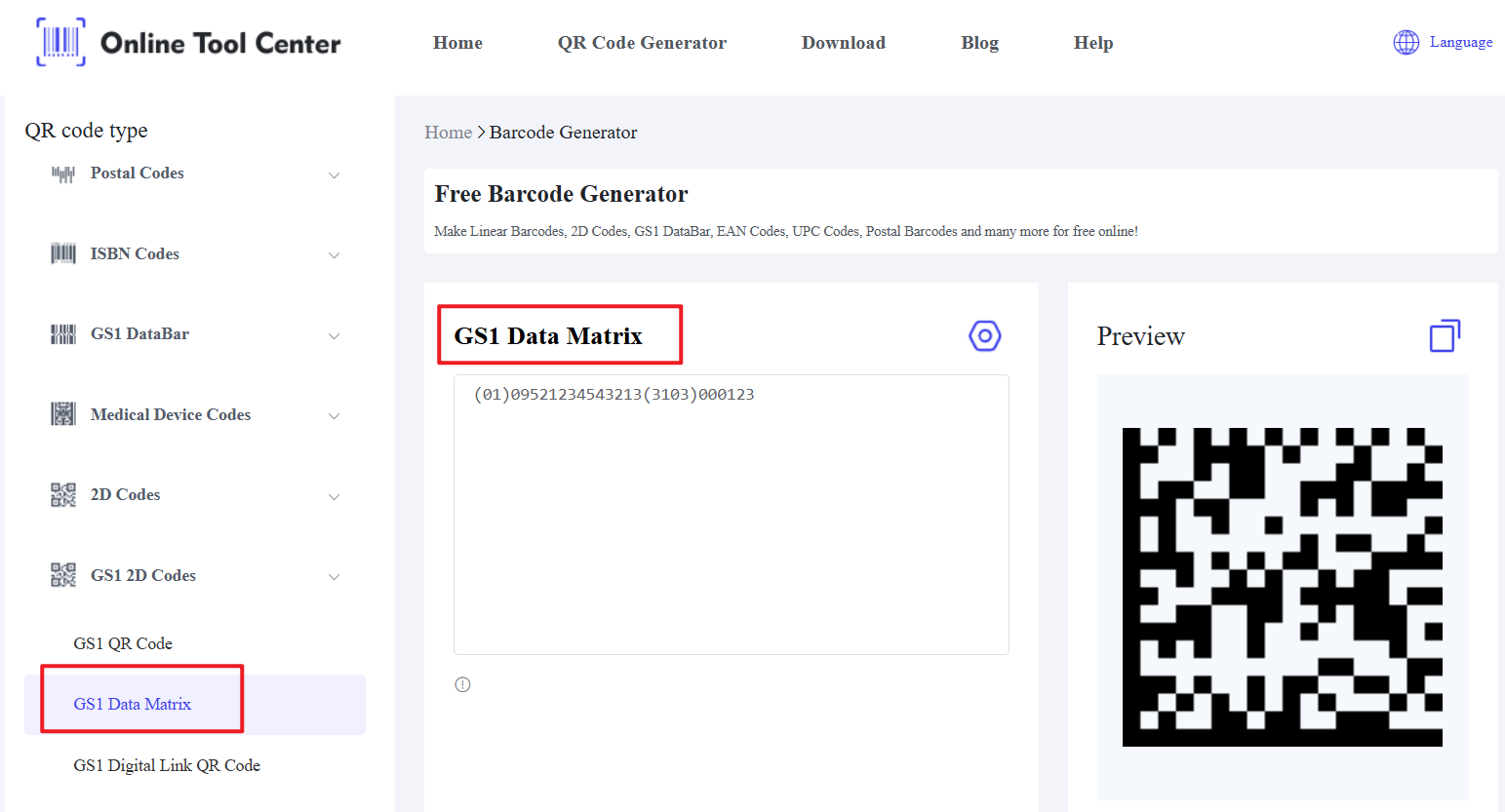
2. Application: The IMb is applied to letters and flat mail to facilitate sorting and delivery within the USPS system. The IMmb, however, is specifically designed to enhance the readability of barcodes on packages, especially those with irregular shapes or packaging that may become distorted during processing.
3. Data Capacity and Redundancy: The two-dimensional structure of the IMmb allows it to encode the same information as the IMpb but in a more compact form.
Additionally, the IMmb's design enables the placement of multiple barcodes on a single label, providing redundancy that increases the likelihood of successful scans throughout the package's journey.
Benefits of Implementing IMmb
● Enhanced Package Visibility: By incorporating multiple IMmbs on a shipping label, there is an increased chance of successful barcode scans throughout the package's journey, leading to more accurate and timely tracking information.
● Improved Processing Efficiency: The robust design of the IMmb reduces the need for manual handling and rework, as automated systems are more likely to successfully read the barcode on the first pass.
● Customer Satisfaction: Reliable tracking and timely deliveries contribute to higher customer satisfaction, as recipients can access accurate information about their packages' statuses.
Steps to Create and Implement an Intelligent Mail Matrix Barcode
1. Review USPS Technical Specifications:
Begin by consulting the USPS's official technical specifications for the IMmb to understand the requirements and guidelines for barcode creation and placement.
2. Prepare Your Data:
Ensure that all necessary information, such as routing codes, unique package identifiers, and service type codes, is accurately compiled and formatted according to USPS standards.
3. Select a Barcode Generator:
Utilize a free online barcode generator that supports GS1 DataMatrix symbology. This tool will assist in encoding your data into the IMmb format, adhering to USPS specifications.
4. Design Your Shipping Label:
Integrate the IMmb into your existing shipping label design, ensuring that it is placed in an area that minimizes the risk of distortion or damage. Consider adding two supplemental IMmbs within unused areas of the label to provide redundancy.
5. Test the Barcode:
Before full-scale implementation, print sample labels and test the barcodes using USPS-approved scanning equipment to confirm readability and data accuracy.
6. Implement in Production:
Once testing is successful, incorporate the IMmb into your standard shipping labels and monitor performance to ensure continued efficiency and accuracy.
Conclusion
The adoption of the Intelligent Mail Matrix Barcode (IMmb) represents a significant advancement in mailing technology, offering enhanced data density, improved error correction, and greater resilience during automated processing.
By following USPS guidelines and utilizing online barcode generator, businesses can effectively implement IMmbs to streamline operations and improve package tracking capabilities.




