Understanding the concept of SKU vs barcode and knowing how to use them effectively can significantly enhance your inventory processes.
Recognizing when to use an SKU barcode and leveraging the strengths of each can lead to more precise tracking and streamlined inventory management.
This article aims to compare SKU vs barcode, explore its usage, and provide practical guidance on generating and managing them.
What is an SKU?
An SKU (Stock Keeping Unit), or Stock Keeping Unit, is a unique identifier for each distinct product or item in a business's inventory.
It is a combination of alphanumeric characters that represent specific details about the product, such as its manufacturer, size, color, and other attributes.
SKUs are essential for tracking inventory levels, managing stock, and identifying products quickly.
Purpose and Importance of SKUs in Inventory Management
SKUs play a vital role in inventory management by providing a systematic way to categorize and track products. They help businesses:
● Maintain accurate inventory records
● Simplify the process of ordering and restocking items
● Analyze sales data and identify trends
● Improve customer service by quickly locating products
Examples of SKUs in Various Industries

SKUs are used across various industries, including retail, manufacturing, and healthcare. For example:
● In retail, a clothing store might use SKUs to differentiate between different sizes and colors of a shirt.
● In manufacturing, SKUs help track raw materials and finished goods.
● In healthcare, SKUs can be used to manage pharmaceutical inventory and medical supplies.
How SKUs are Created and Maintained?
Creating SKUs involves developing a coding system that incorporates relevant product information.
Businesses often use software tools to generate and maintain SKUs, ensuring consistency and accuracy. Regular audits and updates are necessary to keep the SKU system effective and up-to-date.
What is a Barcode?
A barcode is a visual representation of data that can be scanned and interpreted by machines.
It consists of a series of parallel lines or patterns that encode information about a product. Barcodes are used to automate the process of identifying and tracking items.
Types of Barcodes
There are several types of barcodes, each serving different purposes:
● UPC (Universal Product Code): Commonly used in retail, especially in the United States.
● EAN (European Article Number): Similar to UPC, but used internationally.
● QR Codes (Quick Response Codes): Two-dimensional barcodes that can store more information and are often used for marketing and mobile applications.
Examples of Barcode Usage in Different Industries
Barcodes are widely used in various industries:
● In retail, barcodes streamline the checkout process and inventory management.
● In logistics, barcodes track packages and shipments.
● In healthcare, barcodes ensure the accurate administration of medications and track patient information.
What are the Differences Between SKU and Barcode?
SKU vs Barcode:
While SKUs are alphanumeric codes created by businesses to categorize products, barcodes are graphical representations of data that can be read by scanners.
SKUs are primarily used for internal inventory management, whereas barcodes facilitate the automation of data entry and product tracking.
How SKUs and Barcodes are Used Differently in Inventory Management?
SKUs help businesses organize and manage their inventory at a granular level, while barcodes enable quick and accurate data capture.
SKUs are essential for tasks like ordering and restocking, while barcodes are crucial for checkout and tracking processes.
1. Advantages and Disadvantages of SKU vs Barcode
Advantages of SKU:
● Customizable to fit business needs
● Detailed product categorization
Disadvantage of SKUs:
● Require manual entry and management
Advantages of Barcodes:
● Automate data capture
● Reduce errors in data entry
Disadvantages of Barcodes:
● Require scanning equipment
● Less customizable than SKUs
2. Visual Comparison: SKU Number vs. Barcode Representation
A visual comparison highlights the structural differences between SKUs and barcodes.
SKUs are typically alphanumeric codes like "ABC123," while barcodes are graphical patterns that represent encoded data.
How do SKU and Barcode Work Together?
Integrating SKU and barcode systems can enhance inventory accuracy and efficiency. SKUs provide detailed product information, while barcodes automate the data capture process, reducing manual errors.
Combining SKUs and barcodes helps businesses maintain accurate inventory records, streamline operations, and improve customer service.
The integration reduces manual entry errors and speeds up processes like restocking and sales tracking.
Methods for Creating SKUs
Creating SKUs involves developing a coding system that reflects product attributes.
Creating SKUs involves developing a systematic coding method that captures essential product attributes, such as type, size, color, and manufacturer.
Businesses typically use specialized software to generate and maintain SKUs, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
A well-organized SKU system aids in efficient inventory management, helping to categorize products effectively and streamline processes like ordering and restocking.
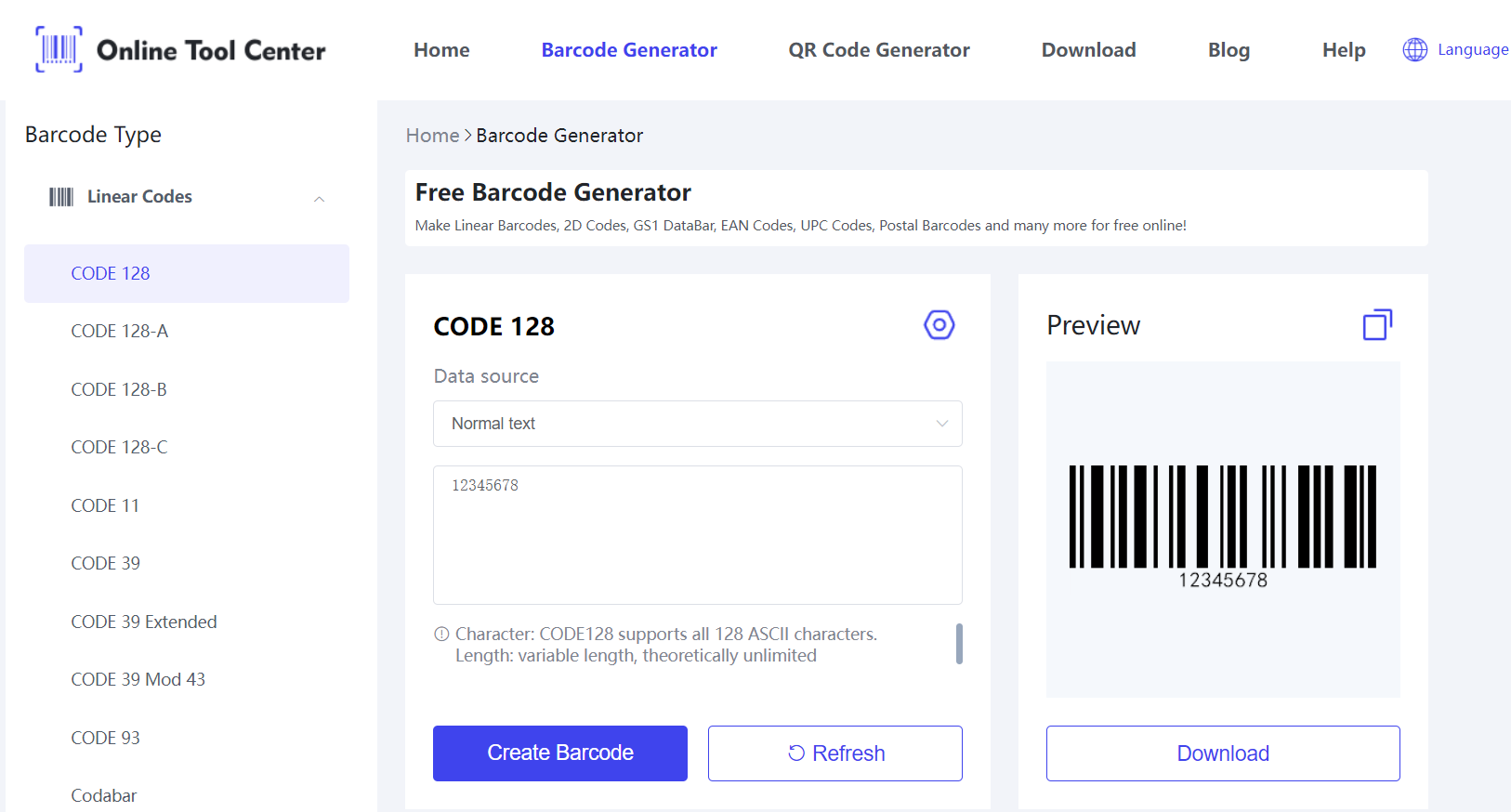
Introduction to Barcode Generation
Barcode generation transforms product information into a scannable format, facilitating quick and accurate data entry. Using a free barcode generator, businesses can easily create various types of barcodes, such as UPC, EAN, and QR codes.
These barcodes enhance inventory management by automating the identification and tracking of products, reducing errors, and improving operational efficiency.
SKU vs Barcode: Which One Should I Choose?
Choosing between SKUs and barcodes depends on your specific inventory management needs.
SKUs are unique alphanumeric codes that help businesses categorize products based on attributes like size, color, and manufacturer. They are crucial for detailed inventory tracking, ordering, and restocking, making them essential for internal organization and management.
Barcodes, however, are graphical representations of data that can be scanned to automate the identification and tracking of items.
They reduce manual entry errors and speed up processes like checkout and inventory audits.
Barcodes are ideal for quick and accurate data capture in retail, logistics, and healthcare. For optimal inventory management, combining both SKUs and barcodes is often the best solution.
Best Practices for Using SKUs and Barcodes
Tips for Effective SKU Management
● Develop a clear and consistent coding system
● Regularly review and update SKUs
● Train staff on the importance of SKUs
Ensuring Barcode Readability and Accuracy
● Use high-quality barcode labels
● Regularly maintain and calibrate barcode scanners
● Conduct periodic audits to ensure accuracy
Regularly review and update SKUs and barcodes to reflect inventory changes and ensure system accuracy.
Provide comprehensive training to staff on how to create, manage, and use SKUs and barcodes effectively.
FAQs
1. What is an example of an SKU Number?
An example of an SKU number could be "SHRT-BLU-M," representing a medium blue shirt.
2. What is the Main Difference Between an SKU and a Barcode?
The main difference is that SKUs are alphanumeric codes created by businesses to categorize products, while barcodes are graphical representations used to automate data capture.
In summary, understanding SKU vs barcode can significantly improve your inventory management processes.
By implementing best practices and utilizing the right tools, such as an SKU barcode system, businesses can achieve greater accuracy and efficiency.
Explore the free barcode generator to streamline your inventory management today.




